A pregnancy is regarded as full-term by the time a woman reaches the 37th week. The baby’s digestive system is fully functional and contains meconium, a sticky, green-colored substance that the baby will pass as the first stool after it is born.
The meconium may contain some lanugo, the fine, downy hair the baby has now shed that used to protect its delicate skin while inside the womb.
During these last weeks of pregnancy, the baby’s head should move down towards the pelvis, at which point the head is said to be “engaged.” Once this happens, the mother may notice that the bump in her tummy moves down slightly.
On some occasions, the head only becomes engaged as labor begins. The majority of women go into labour between weeks 38 and weeks 42 of pregnancy.
Babies usually weigh an average of 3 to 4 kg by this late stage of pregnancy.
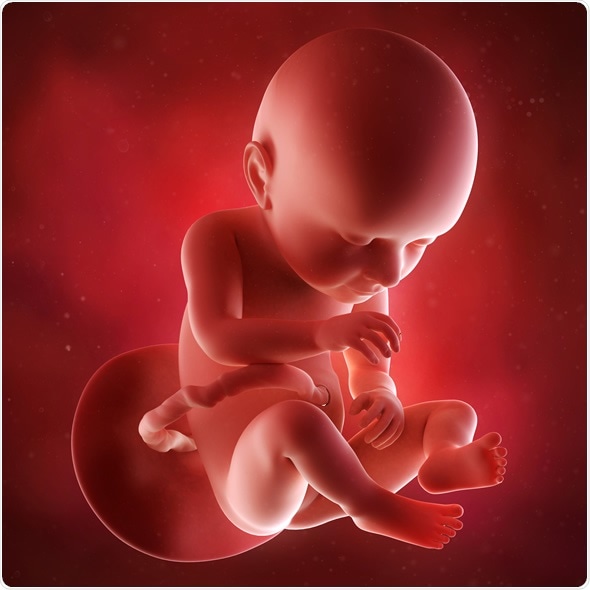
Week 37
By week 37, the baby’s organs are ready to function independently. The baby may have become engaged in the pelvis, particularly in cases of first pregnancy.
Second or subsequent babies are more likely to become engaged at a later stage because the mother’s pelvic bones are positioned slightly differently.
The baby is still growing rapidly and could gain as much as an additional two pounds during the last four weeks of pregnancy.
Medical accurate 3d illustration of a fetus week 37. Image Copyright: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock
Week 38
By week 38 of pregnancy, the baby has developed a firm hand grip and their toenails have reached the tips of their toes. By this point, the baby has shed almost all of their lanugo.
The brain weighs around 400 grams and will continue to grow after the baby is born. The baby may weigh up to 6.5 pounds. The mother’s weight usually remains stable during the last couple of weeks of pregnancy.
Week 39
Theoretically, week 39 is the last week of pregnancy, although it could take a little longer for the mother to go into labor, particularly in cases of the first pregnancy.
There is now very little space in the uterus and the mother may have noticed that her baby’s movements have slowed down completely.
The placenta continues to supply the baby with the antibodies it will require to combat infection once it is born. If a mother chooses to breastfeed her baby, then her milk will provide extra antibodies.
The baby’s skull bones are now prepared for the journey through the birth canal. They can move over each other and overlap to protect the brain while the head passes through the cervix.
The cervix is now softening and the mucus plug which had previously been keeping the cervix “sealed” may now be released as labor approaches.
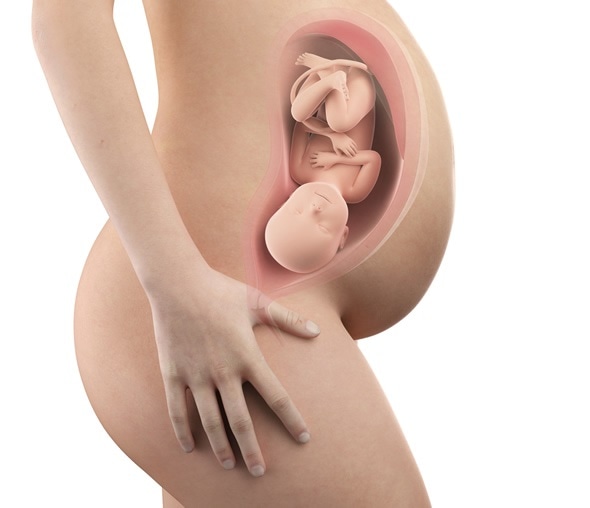
Week 40
Forty weeks into pregnancy, the baby is now fully grown and prepared for birth. The baby may be around 500 mm long and weigh 6.5 pounds or more, although healthy babies can still vary in size considerably.
Pregnant woman with visible uterus and fetus week 40. Image Copyright: Sebastian Kaulitzki / Shutterstock
Mothers should not be alarmed if their due date passes without them going into labor, as only a small number of babies are born on the due date and it is just as usual for a baby to arrive one or two weeks late as it is for a baby to be born one or two weeks early.
Further Reading